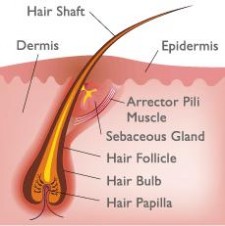
Your hair is one of the most important parts of your body. Hair is an outgrowth of filamentous cells, containing keratin, that grows from follicles found in the dermis.The human body, apart from the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair ‘ short, fine, lightly colored and barely noticed hair that develop everywhere on the human body. Hair often refers to two distinct structures: the part beneath the skin is called a hair follicle or when pulled from the head is called a bulb. How is a typical hair shaft structured? It is essentially nothing but dead shaft seen above the scalp. A typical hair shaft is made up of three essential layers i.e. cuticle, medulla and cortex. The cuticle is the outermost layer. This protects the medulla and cortex. To put it simply cuticle is a transparent structure and only this layer will give a shiny appearance. If this outer layer is not healthy then you will still get dull appearance. Medulla is the innermost layer constituted by large size cells. Cortex also constitutes the middle layer. This possesses a protein called keratin and coloring pigments. The cortex determines the shape and size of the hair shaft.
Keratin- The Main Constituent
Keratin refers to a family of fibrous structural proteins. It is an intermediate filament; when assembled in bundles, it is tough and insoluble forming hard, unmineralized structures found in a variety of species including reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Nails are also constituted mainly by keratin. Other constituents of hair include the pigment called melanin (responsible for hair color), certain fat, small quantity of vitamins and traces of minerals like zinc etc. Hair also includes 10 to 15 per cent of water which helps maintain moisture and balance? biochemical and physiological properties.
Hair Follicle
The other part of your hair is the hair follicle. Sunk beneath your scalp, it is encircled by two protective sheaths the inner sheath and the outer sheath. The hair shaft is protected well by these two sheaths. Connected to the hair shaft is a sebaceous gland, a tiny sebum-producing gland found everywhere except on the palms, lips and soles of the feet. Thicker the density of the hair, the more the number of sebaceous glands which can be found. Sebum(Latin: fat or tallow) is made of fat (lipids), wax, and the debris of dead fat-producing cells. The older you are the less sebum you produce. Women produce lesser sebum as they grow older. Men also produce less sebum but it is more compared to women. Hair shaft has its root in the follicle. In fact the hair shaft comes out from the follicle. There is a projection called hair papillae at the bottom. Hair papillae have tiny blood capillaries to nourish my hair root. Thickness of the shaft totally depends up on follicle size. Follicle is therefore responsible for the health of the hair shaft. Follicle can support its nourishment till the shaft is pushed out of the follicle base.
Hair Follicle Cycle
Hair growth on your scalp is around six inches per year. Hair growth will be around 0.03 to 0.04 mm only. Hair growth is random. Growth is neither cyclical or seasonal. This involves three stages: (1). Anagen, (2). Catagen, and (3). Telogen.
Anagen
This is the active hair growth phase. Growth of new hairs is done and hair follicles push out club hairs out of your follicles. Hair grown during this growth phase will remain for about two to six years. Some of you might have felt problem of hair growing beyond certain length. This may be due to short phase of growth (Anagen). Long hair is due to long phase of growth. Also there is short active hair growth phase on? arm pits, limbs, eyelashes, and eyebrows about 30-45 days. Active phase of growth is not warranted at these regions.
Catagen
This is the transitional phase. Atagen is the phase that follows active hair growth phase called Anagen. Once anagen phase gets completed your hair undergoes a transitional stage. About three per cent of your hair undergoes a transitional process at any given period of time. This phase will lasts for about a period of three to four weeks. During catagen hair growth gets stopped. The outer sheath of your hair root undergoes a shrinking process. Then your hair gets attached firmly.
Telogen
This is the resting phase. Telogen is the phase that follows a transitional phase called Catagen. There is a resting period for your hair. About 10-15 per cent of all your hairs undergo a resting process at any given period of time. Telogen is the resting phase and accounts for 10-15% of all hair. This phase will last for about a period of 100 days (on your scalp) and it will be more than 100 days for hair on your limbs, armpits, eyelashes, eyebrows etc.
Keratin- The Main Constituent
Keratin refers to a family of fibrous structural proteins. It is an intermediate filament; when assembled in bundles, it is tough and insoluble forming hard, unmineralized structures found in a variety of species including reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Nails are also constituted mainly by keratin. Other constituents of hair include the pigment called melanin (responsible for hair color), certain fat, small quantity of vitamins and traces of minerals like zinc etc. Hair also includes 10 to 15 per cent of water which helps maintain moisture and balance? biochemical and physiological properties.
Hair Follicle
The other part of your hair is the hair follicle. Sunk beneath your scalp, it is encircled by two protective sheaths the inner sheath and the outer sheath. The hair shaft is protected well by these two sheaths. Connected to the hair shaft is a sebaceous gland, a tiny sebum-producing gland found everywhere except on the palms, lips and soles of the feet. Thicker the density of the hair, the more the number of sebaceous glands which can be found. Sebum(Latin: fat or tallow) is made of fat (lipids), wax, and the debris of dead fat-producing cells. The older you are the less sebum you produce. Women produce lesser sebum as they grow older. Men also produce less sebum but it is more compared to women. Hair shaft has its root in the follicle. In fact the hair shaft comes out from the follicle. There is a projection called hair papillae at the bottom. Hair papillae have tiny blood capillaries to nourish my hair root. Thickness of the shaft totally depends up on follicle size. Follicle is therefore responsible for the health of the hair shaft. Follicle can support its nourishment till the shaft is pushed out of the follicle base.
Hair Follicle Cycle
Hair growth on your scalp is around six inches per year. Hair growth will be around 0.03 to 0.04 mm only. Hair growth is random. Growth is neither cyclical or seasonal. This involves three stages: (1). Anagen, (2). Catagen, and (3). Telogen.
Anagen
This is the active hair growth phase. Growth of new hairs is done and hair follicles push out club hairs out of your follicles. Hair grown during this growth phase will remain for about two to six years. Some of you might have felt problem of hair growing beyond certain length. This may be due to short phase of growth (Anagen). Long hair is due to long phase of growth. Also there is short active hair growth phase on? arm pits, limbs, eyelashes, and eyebrows about 30-45 days. Active phase of growth is not warranted at these regions.
Catagen
This is the transitional phase. Atagen is the phase that follows active hair growth phase called Anagen. Once anagen phase gets completed your hair undergoes a transitional stage. About three per cent of your hair undergoes a transitional process at any given period of time. This phase will lasts for about a period of three to four weeks. During catagen hair growth gets stopped. The outer sheath of your hair root undergoes a shrinking process. Then your hair gets attached firmly.
Telogen
This is the resting phase. Telogen is the phase that follows a transitional phase called Catagen. There is a resting period for your hair. About 10-15 per cent of all your hairs undergo a resting process at any given period of time. Telogen is the resting phase and accounts for 10-15% of all hair. This phase will last for about a period of 100 days (on your scalp) and it will be more than 100 days for hair on your limbs, armpits, eyelashes, eyebrows etc.